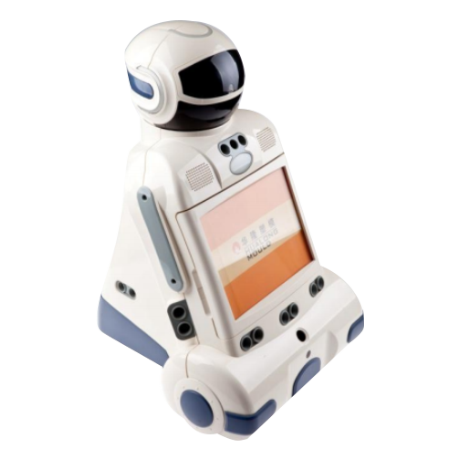
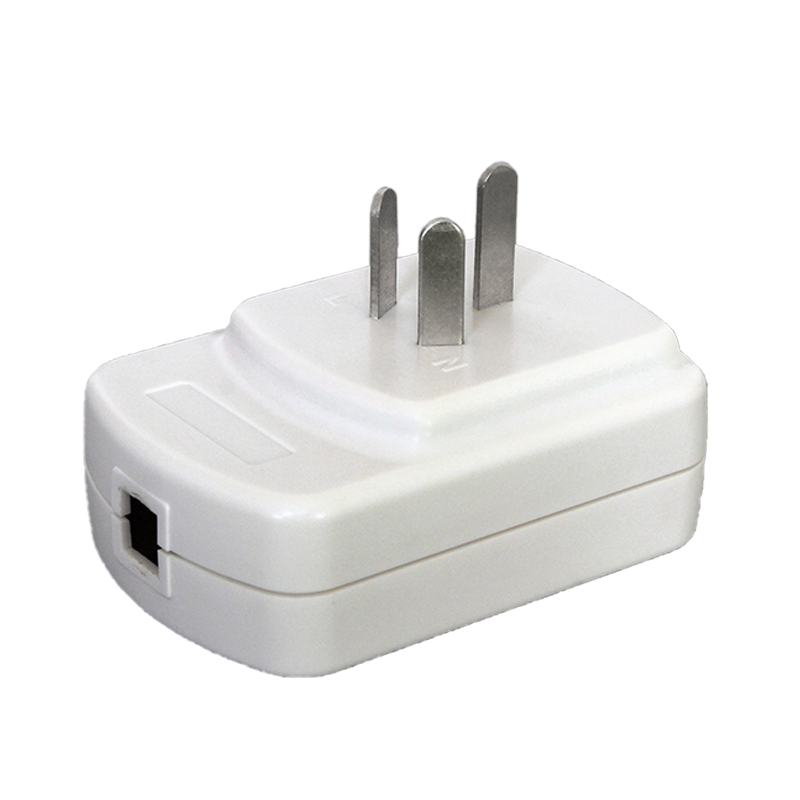
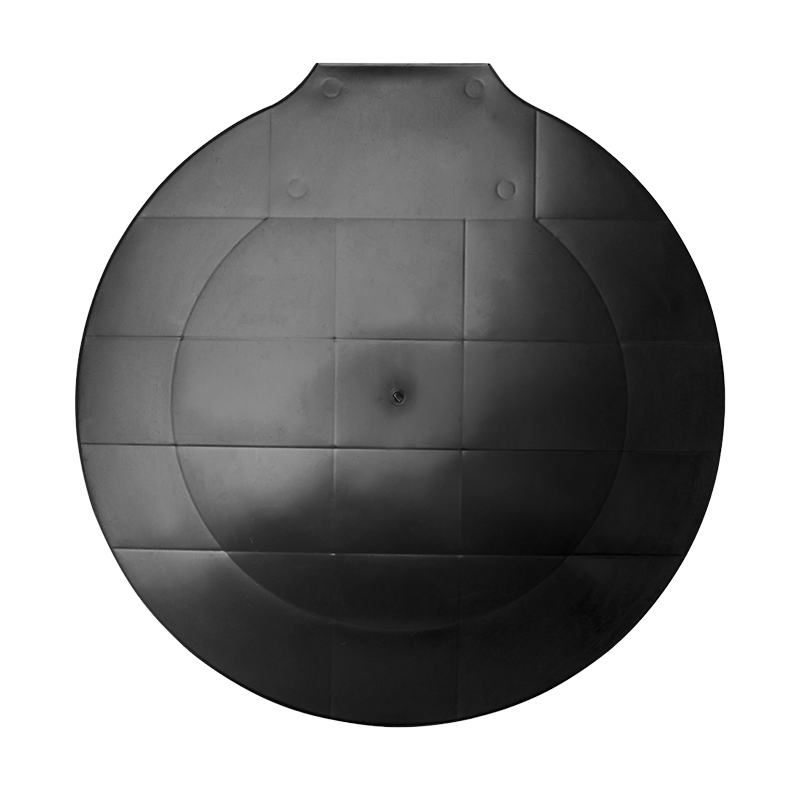
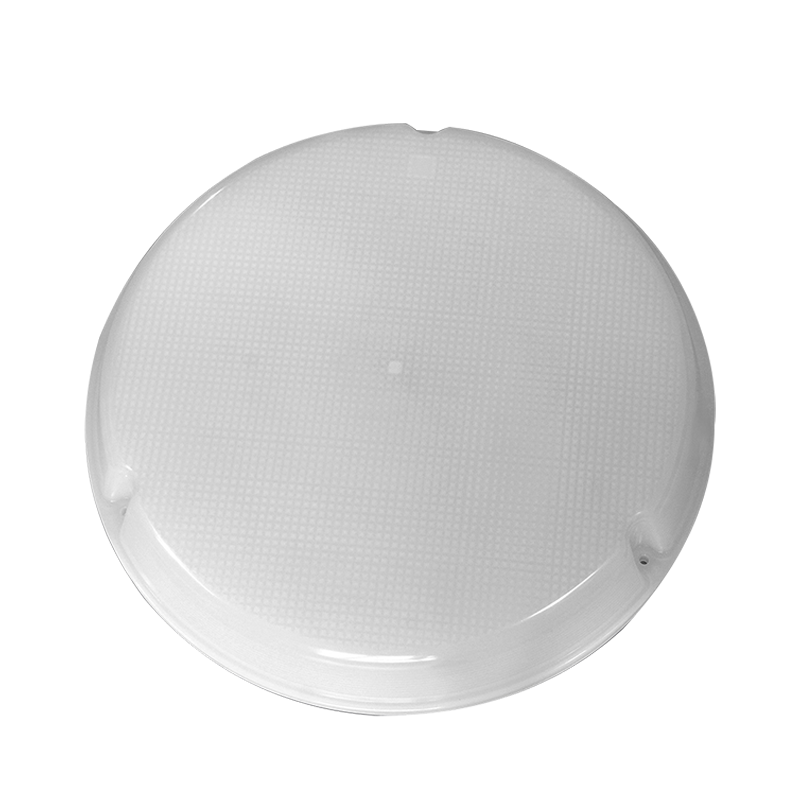
Plastic injection molding, as an important part of the plastic processing industry, is a plastic product made by injection molding technology. Injection molding is a processing method that injects molten plastic into the mold cavity, cools and solidifies it, and then demolds it to obtain the desired shape and size of the product. The application range of injection molding parts is extremely wide, from tableware, toys, and household items in daily life, to the shell and internal structural parts of electronic products, to interior parts, exterior parts, functional parts in automobile manufacturing, and various plastic parts in medical devices.
The key elements of the injection molding process include mold design and manufacturing, material selection, injection molding machine operation, etc. The mold is the core component of injection molding, and its design accuracy and manufacturing quality directly affect the shape, size, surface quality and other aspects of the injection molded parts. Mold design needs to consider factors such as the structural characteristics of the product, wall thickness uniformity, demolding slope, and fillet processing to ensure that the injection molded parts can be demolded smoothly and meet the design requirements. The selection of injection molding materials needs to be comprehensively considered based on the product's use requirements, processing performance, cost and other factors. Common injection molding materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS), etc. Different materials have different physical and chemical properties, such as hardness, toughness, heat resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, etc., and they need to be reasonably selected according to specific needs. The injection molding machine is the key equipment for injection molding, and its performance directly affects the production efficiency and product quality of the injection molded parts. The injection molding machine needs to have precise temperature control, pressure control, speed control and other functions to ensure that the molten plastic can be evenly and stably injected into the mold cavity.
Injection molded parts are widely used in many fields due to their excellent physical properties and processing properties. With the continuous advancement of science and technology and the improvement of people's living standards, the application field of injection molded parts is also constantly expanding. With the popularization of electronic products such as smart phones, tablets, and laptops, injection molded parts are more and more widely used in electronic products. For example, mobile phone shells, keyboard keys, display frames and other parts are all made by injection molding. These parts not only require exquisite appearance and precise size, but also good wear resistance, corrosion resistance and other characteristics.
Injection molded parts are also widely used in automobile manufacturing, such as interior parts (dashboards, door panels, seats, etc.), exterior parts (bumpers, headlight housings, etc.), functional parts (fuel tanks, water tanks, etc.), etc. The application of injection molded parts in automobile manufacturing not only reduces the weight of the car body and improves fuel economy, but also enhances the comfort and safety of the car. The application of injection molded parts in medical devices is also very important, such as syringes, infusion bottles, medical device housings and other parts. These parts are required to have good biocompatibility, non-toxic and harmless characteristics to ensure the safety and health of patients. Injection molded parts are also widely used in daily life, such as tableware, toys, household items, etc. These parts not only require beautiful appearance and good durability, but also need to meet relevant safety standards and environmental protection requirements.
After more than 30 years of unremitting efforts, our company has developed into a professional manufacturer mainly engaged in mold manufacturing and plastic product processing. We provide one-stop services from product development, mold design and manufacturing, plastic injection molding to finished product assembly, and can tailor high-quality plastic accessories injection molded parts for customers. Our customers are all over Europe and the United States. High-quality brands and well-known listed companies at home and abroad, customized products involve various instruments and meters, equipment accessories, industrial automation and IoT smart devices, auto parts, kitchen appliances, household items and other fields. These products are widely used in different fields such as electricity, communications, security, automobiles, aerospace, medical, life, etc., meeting the diverse needs of customers.

 English
English Español
Español 简体中文
简体中文